Introduction
Microsoft Excel is one of the most powerful tools for financial analysis, data management, and reporting. However, even experienced users encounter frustrating Excel errors that disrupt formulas and calculations.
Understanding what each error means and how to fix it can save you hours of troubleshooting. In this guide, we’ll explore the most common Excel errors, explain why they happen, and show you exactly how to fix them using real examples and screenshots in a simple way.
Excel displays error codes when something goes wrong in a formula. These errors can occur because of:
- Incorrect cell references.
- Invalid data types.
- Missing values.
- Division by zero.
- Typing mistake in formula names or ranges.
Fortunately, every error message has a specific meaning and once you understand the cause, fixing it becomes simple.
Here, I have covered only seven common ones but there are some more errors that occurs in excel which will be discussed later on.
1. #DIV/0! Error
Means:
This error occurs when a number is divided by zero or by an empty cell.
Example:
Formula: =A2/B2 , If B2= 0, then Excel returns as: #DIV/0!
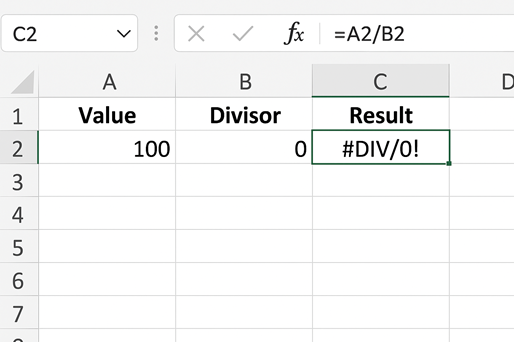
How to Solve:
Ensure the denominator is not zero or blank.
You can also use the IFERROR or IF function as shown below for better presentation of data.
=IF(B2=0,””,A2/B2), this means that if B2 is having digit 0, then give me a blank cell else give the actual result.
=IFERROR(A2/B2, “NA”), this means that if any error occurs then just give NA( not applicable) so that data looks clean. Remember this is not to solve that error.
2. #VALUE! Error
Means:
This happens when Excel expects a number but finds text instead.
Example:
Formula: =A2*B2 ,If A2 = “Profit” and B2 = 100, Excel returns as #VALUE!
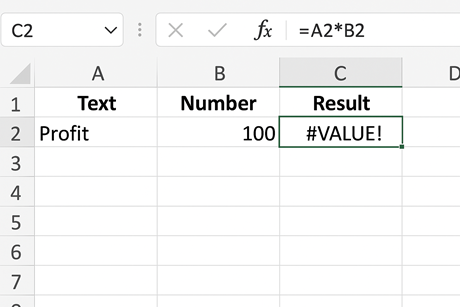
How to Solve:
Check for text or spaces in numeric cells. Replace text with a numeric value and the error will be corrected.
3. #REF! Error
Means:
This appears when a referenced cell is deleted or moved.
Example:
Formula: =A2+B2 and you delete column B, Excel returns as #REF!.
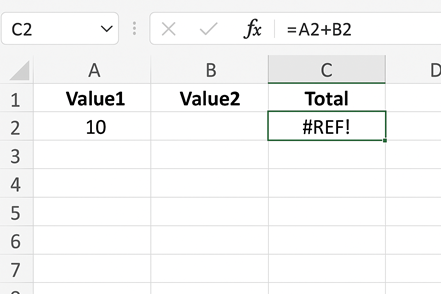
How to Solve: Avoid deleting cells used in formulas. Restore references manually or use named ranges.
4. #NAME? Error
Means:
This means Excel doesn’t recognize something in the formula often a typing mistake in the function name or a missing range name.
Example:
Formula: =SUMM(A1:A5), Excel returns as #NAME?
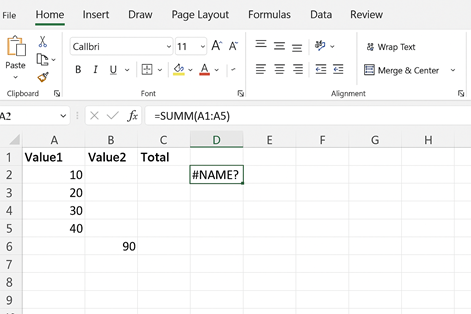
How to Solve:
Correct the function name to =SUM(A1:A5) or check that named ranges exist.
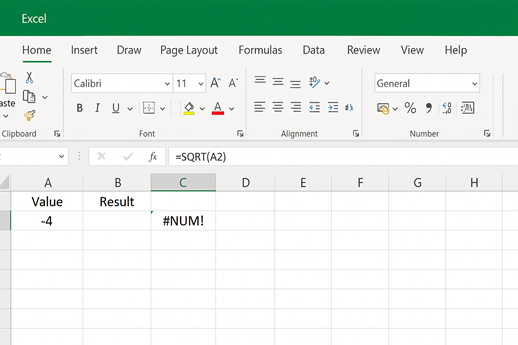
5. #NUM! Error
Means:
Occurs when a formula contains an invalid numeric value e.g., square root of a negative number.
Example:
Formula: =SQRT(A2), Excel returns as #NUM!
How to Solve:
Ensure numbers are valid. Use “IF” formula as shown in example at beginning, to check before doing calculation as:
Formula: =IF(A2<0,”Invalid”,SQRT(A2))
Here, it means that if A2 has digit which is less than 0, then show as invalid in cell else its square root.
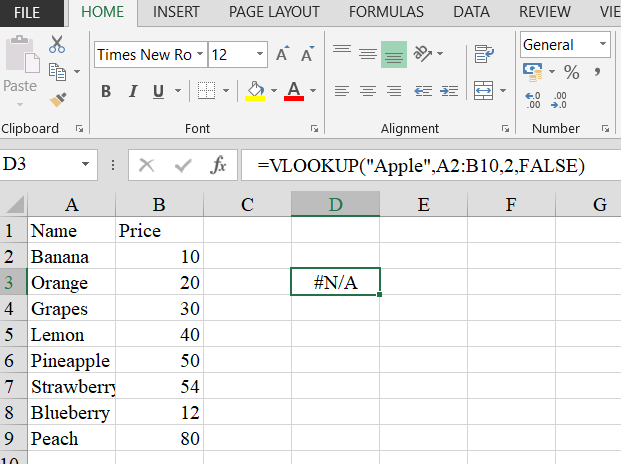
6. #N/A Error
Means:
Excel can’t find what you’re looking for, often in lookup formulas like VLOOKUP or MATCH functions.
Example:
Formula: =VLOOKUP(“Apple”,A2:B10,2,FALSE)
Here, If “Apple” isn’t in A2:A10 then cell will show #N/A.
How to Solve:
Check lookup ranges and spellings. Here also we can use IFERROR formula to handle missing data as:
Formula: = IFERROR (VLOOKUP(“Apple”,A2:B10,2,FALSE),”Not Found”) Here, cell will show Not Found as result instead of the error.
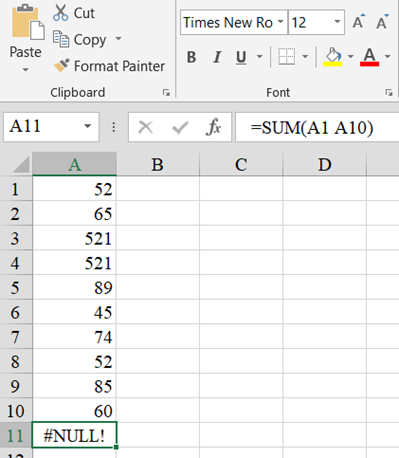
7. #NULL! Error
Means:
Appears when you use a space instead of a comma or colon in a range, in other way using a incompatible cell address.
Example:
Formula: =SUM(A1 A10). This is wrong.
Formula: =SUM(A1:A10).This is correct.
How to Solve:
Check your range separators i.e.( that is) use colons (:) for ranges and commas (,) for multiple arguments.
Conclusion
Understanding Excel errors is crucial for anyone managing data or financial models. By learning what each error means and how to fix it, you can make your spreadsheets more reliable and professional.
Remember:
- Check your formula references.
- Avoid blank cells in calculations.
- Use IFERROR and IFNA to handle exceptions gracefully.
Mastering error handling in Excel saves time and boosts confidence in your data accuracy.



